From Windows Server 2008, there are new "Shrink Volume" and Extend Volume to help resize partition without losing data. However, not all partitions can be resized. Many people feedback that "Extend Volume" is disabled after shrinking or even deleting other partition. This article introduces why Extend Volume is disabled in Windows Server 2008/2012/2016/2019/2022 and what to do when Extend Volume is disabled for C drive.

Why Extend Volume is disabled for system C drive
To system partition C: drive, there are two common reasons why Extend Volume option is disabled in Server 2008/2012/2016/2019/2022.
1. No contiguous unallocated space on the right
Firstly, you should know that the size of a disk is fixed (except VMware VMDK and Hyper-V VHD virtual disk), so before extending C drive, you have to delete or shrink other volume to get unallocated space. If you right click C drive without such kind of space, of course Extend Volume option is disabled for C drive.
The problem is, Extend Volume is always disabled for system partition C after shrinking D or other volume, this is because:
Extend Volume only works when there is contiguous unallocated space on the right, but you can't get such required space via other Shrink volume function.
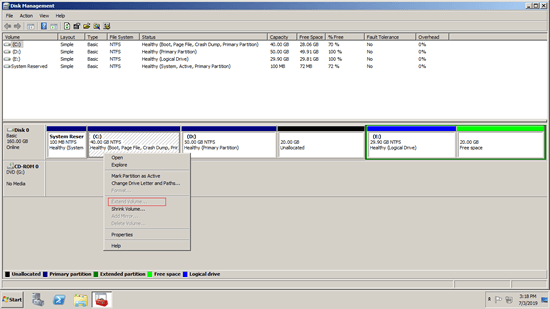
As you see in the screenshot, the 20GB unallocated and Free space are shrunk from drive D: and E. Both space are nonadjacent to C drive, therefore, Extend Volume is grayed out.
In this case, you need a tool to move unallocated space to behind C: drive. When there's right adjacent unallocated space, Extend Volume will be enabled for C drive.
2. The right contiguous partition (D:) is logical
Cannot get required unallocated space, some people try to delete the right contiguous partition. It works if you use GPT type hard disk. If you use MBR style disk and D is primary partition, it also works. But if D is a logical partition, Extend Volume is still disabled for C drive even after deleting D.
Unlike GPT disk that all partitions are created as primary, In MBR disk, there could be maximum 4 primary partitions or 3 plus an extended partition.
Unlike primary partition that works independently, logical drive will be converted to free space after deleting, which is still part of Extended partition.
In Disk Management, unallocated space that deleted from primary partition can't be extended to any logical partition. Free space that deleted from logical drive can't be extended to any primary partition.
System partition C is primary in most cases, so you can't extend it by deleting the contiguous logical partition.
To convert the Free space to unallocated, you have to delete all other logical and the Extended partition.
Why Extend Volume is disabled for D or other data partition
To data volumes such as D, there are same issue. Disk Management cannot extend D drive by shrinking system partition C or other data partition. If the partition type of the right contiguous drive E is different, Extend Volume option is disabled for D drive after deleting E. (For example, D is primary and E is logical)
To data volumes, there's an additional reason, Extend Volume can only expand the partitions that are formatted with NTFS or without file system.
Another common FAT32 as well as any other types of partitions are not supported.
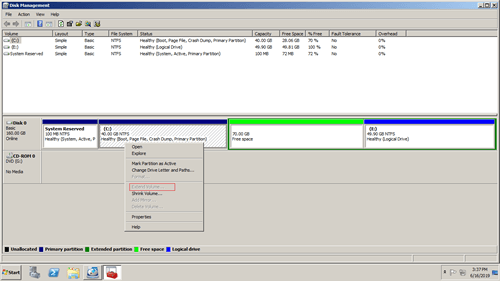
As you see in the screenshot, Extend Volume is disabled for D drive, although there is adjacent unallocated space on the right.
What to do when Extend Volume option is disabled
In fact, it is easy to fix the Extend Volume disabled issue for Windows 2008 server.
- If you got unallocated space but it is nonadjacent to the drive that you want to extend, run NIUBI Partition Editor and move unallocated space to be contiguous on either side.
- To shrink and extend NTFS or FAT32 partition, shrink and extend primary or logical partition, there is no difference to NIUBI.
Video guide to fix Extend Volume is disabled in Windows Server 2008 R2/2012/2016/2019/2022:
Right click any NTFS or FAT32, primary or logical partition and then select "Resize/Move Volume".
- Drag either border towards the other one, then you can shrink this partition.
- Drag the middle towards other side, then you can move this partition and associated unallocated space.
- Drag the border opposite to the other one, then you can combine contiguous unallocated space to this partition.
As a disk partition management software, NIUBI Partition Editor helps do many other operations.