Like other versions of Windows, the C: drive is running out of space on Windows Server 2025. This issue is frustrating, as you may not know how to resolve it or might be troubled by it again in the near future. If you search on Google, you may find over 10 methods to free up disk space on Windows servers. However, there's no need to try all or most of these methods, as you could spend a lot of time with little result. This article explains why the C: drive is running out of space and how to resolve the issue quickly and effectively on Windows Server 2025.

Why is C drive running out of space on Server 2025
Some viruses or Windows errors may cause the disk space usage to be calculated incorrectly, but this is rare. In most servers, the C: drive is filling up due to a variety of files, including those produced by Windows, required by the server, and junk or unnecessary files.
- Application Installations: Many programs are often installed on the C: drive by default. This can result in the C: drive filling up quickly, especially if the programs are large or frequently updated.
- Temporary Files: Applications, browsers, and even Windows itself create temporary files. Over time, these can pile up and consume a lot of space.
- Windows Updates: Regular updates from Microsoft can accumulate over time, especially if old update files are not cleaned up. This can take up significant space on the C: drive.
- Large User Profiles or Downloads: Sometimes, user data (such as documents, downloads, or videos) can be stored on the C: drive, leading to it filling up quickly.
- Log Files: System logs and application logs can accumulate over time, especially on servers that run continuously or handle many tasks. These logs can take up considerable space if not managed properly.
- Junk and Unnecessary Files: Files such as cached browser data, old installer files, and other leftovers from uninstalled programs can accumulate and take up unnecessary space.
- Paging Files and Hibernation Files: Windows uses a paging file (virtual memory) to extend RAM, which can be quite large, especially if your system has a lot of RAM. Hibernation files (if enabled) can also take up significant space on the C: drive.
- Shadow Copies/Backup Files: Shadow copies, created for file versioning and backup, can use significant space on the C: drive if not managed properly.
- System Restore Points: Windows automatically creates restore points, which are snapshots of system configurations. These can consume a lot of space, especially on systems with frequent updates or installations.
Delete various of unnecessary files to reclaim disk space
All the files listed above can be deleted, and the disk space they occupy will become usable again. However, the methods for deleting these files vary. For paging files, you need to change their location and reset them manually. For shadow copies and restore points, you need to delete or reset them yourself as well. For other types of files, you can easily delete them using Windows built-in "Disk Cleanup" tool.
To delete files with Disk Cleanup when C drive is running out of space on Windows Server 2025:
- Press Windows + R on the keyboard, type "cleanmgr" and press "Enter".
- C: drive is selected by defaut, simply click OK to continue.
- Disk Cleanup will calculate how much space can be freed. In the next window, select the unnecessary files to delete and click OK.
- Click the "Delete Files" button to confirm the deletion.
To delete shadow copies and restore points:
- Open Window File Explorer
- Right click C drive and click "Properties", and then switch to "Shadow Copies" on the top.
- Select the previous copies and click "Delete Now".
To remove paging files from C drive:
- Press Windows and R on keyboard, type sysdm.cpl ,3 and press Enter.
- Click "Settings" under "Performance" in "Advanced" tab.
- Switch to "Advanced" tab on the top.
- Click "Change" under "Virtual Memory".
- Uncheck "Automatically manage paging file size for all drives" on the top.
- Select D: or other drive, enter amount of "Initial size" and "Maximum size" in "Customer size" radio box, and then click "Set".
- Select C: drive and select "No paging file" radio box, then click Set.
- Click OK.
If you don't want to delete files or make changes to the server, or if you cannot free up a large amount of space, there’s a better method: move free space from other partitions. This approach has two significant benefits: the operating system, programs, settings, and everything else remain unchanged, and you'll gain a large amount of free space without worrying about the C: drive running out of space on Windows Server 2025 again. You can use this method alone to resolve the issue or as a supplement to other solutions.
Move free space to C drive from other partitions
To accomplish this task, the reliable disk partition software is required. Compared to other disk partition software, NIUBI Partition Editor is much safer and faster because of its powerful technologies:
- Hot Clone: Clone disk partitions without interrupting the server. You can clone the system disk before making changes or as part of a regular backup routine.
- Virtual Mode: To prevent mistakes, all operations are listed as pending for preview. Real disk partitions are not changed until you click "Apply" to confirm.
- Cancel-at-will: If you apply incorrect operations, you can cancel ongoing tasks without worrying about partition damage.
- 1 Second Rollback: If any error is detected while resizing partitions, the software can automatically revert the server to its original state in an instant.
- Advanced File-Moving Algorithm: Resize and move partitions 30% to 300% faster, saving significant time, especially when handling a large number of files.
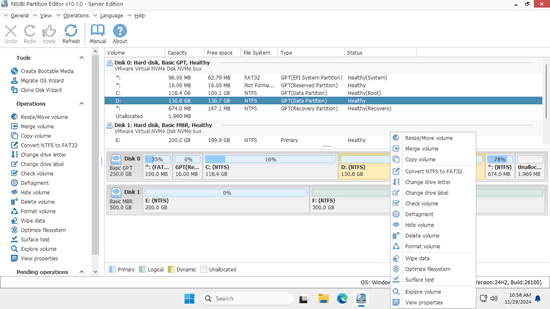
Download NIUBI Partition Editor, and you'll see all storage devices, along with their partition layouts and detailed information in the main window. Right-click a partition or the front of a disk, and you'll see the available options.
To move free space from another partition to the C: drive, you only need the "Resize/Move Volume" feature. Shrink the D: drive or another partition to create unallocated space on the left, and then merge this unallocated space with the C: drive. To accomplish this, simply drag and drop on the disk map. Follow the steps in the video to move free space to the C: drive.
When the C: drive is running out of space on Server 2025, extend it as much as possible. In addition to shrinking and extending partitions on Windows Server 2025 and previous versions, NIUBI Partition Editor helps you perform many other disk partition management operations. Explore the detailed features of this tool or watch the video tutorial to learn how to use it.