Storage device is an indispensable component to a server, no matter you use SSD, mechanical HDD or hardware RAID array. To initialize disk, create, move and resize partitions, you need a reliable disk management tool. Windows Server 2008 R2 has inbuilt "Disk Management". It can do some basic operations such as create, delete and format partition. Better than previous version, it can shrink and extend partition, but the ability is limited. This article introduces how to run Disk Management in Windows Server 2008 R2 and its shortages.

1. How to open Disk Management in Server 2008 (R2)
There are 2 common ways to open Disk Management in Windows Server 2008 R2:
- Press Windows and R together on the keyboard, type diskmgmt.msc and press Enter.
- Click Server Manager on bottom left of the screen behind Windows logo, and then switch to "Storage" > "Disk Management".
2. Basic features of Windows Server 2008 R2 Disk Management
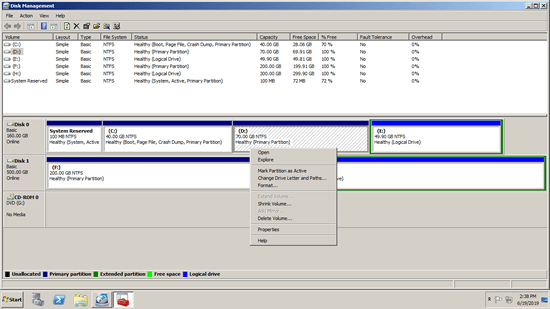
After opening Disk Management, right click a partition or the front of a disk, then you'll see the available operations:
To a brand new hard disk:
- Online, offline
- Initialize.
Hard disk must be online and initialized before creating new volume.
To unallocated space:
Create new volumes.
To an allocated partition:
- Open root directory in File Explorer
- Mark partition as Active
- Change drive letter and path
- Format partition
- Delete partition
3. Advanced features of Windows Server 2008 Disk Management
Manage dynamic volumes:
It is able to create and manage Simple, Mirrored, Stripped, Spanned and RAID 5 dynamic volume.
Dynamic disk volumes consume much resources and decrease server performance. Because hardware price is much cheaper now, most of servers use hardware RAID arrays instead of dynamic volume.
Disk conversion:
Disk Management has the option to convert disk between MBR and GPT, but you must delete all partitions on the disk in advance.
It can only convert Basic disk to Dynamic without losing data. To convert Dynamic disk to Basic, you must delete all partitions on the disk, too.
Change partition size:
Better than previous version, Server 2008 Disk Management has new Shrink and Extend Volume feature to help resize partition without losing data.
Comparing with other advanced features, these new functions are likely to be used. However, you cannot extend a partition by shrinking another one.
How to shrink/extend partition in Server 2008 R2 with Disk Management
Many server administrators need to change partition size after running the server for a period of time.
To shrink partition with Server 2008 Disk Management:
- Follow the method above to open Server 2008 Disk Management tool.
- Right click a NTFS partition and select Shrink Volume.
- Enter and amount of space and click Shrink button.
Disadvantages of Shrink Volume feature:
- Only NTFS partition is supported.
- unallocated space can only be made on the right while shrinking partition.
- It cannot shrink partition beyond the point where unmovable files are located.
To extend partition with Server 2008 Disk Management:
- Right click the partition with adjacent unallocated space on the right, select Extend Volume in the list.
- Simply click Next till Finish in the pop-up Extend Volume Wizard window.
Disadvantages of Extend Volume feature:
- Only NTFS partition is supported.
- There must be adjacent unallocated space on the right of the partition that you want to extend, otherwise, Extend option is disabled.
- If D is logical drive, you still cannot extend C: drive even by deleting D.
4. Best disk partition manager for Server 2008 and R2
There are many disk partition software in the market, but better than other tools, NIUBI Partition Editor is much safer and faster because of its innovative technologies:
- Virtual Mode - all operations you do are listed as pending for preview before clicking "Apply" to take effect.
- Cancel-at-will - if you applied wrong operations, you can cancel the ongoing unwanted operations without damage partitions.
- 1 Second Rollback - if any error is detected while resizing partition, it automatically reverts server to original status in a flash.
- Hot Clone - clone disk partition without server interruption.
- Advanced file-moving algorithm - move and extend partition 30% to 300% faster, saving much time especially when there are large amount of files.
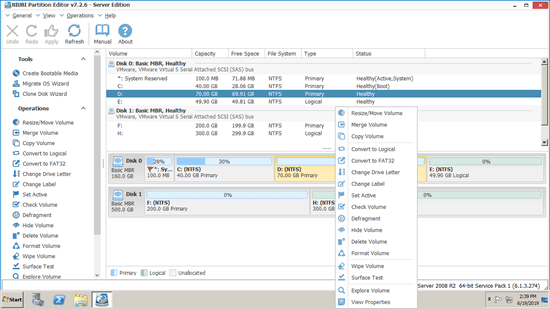
Download this disk management tool and you'll see the main window with disk partition layout and other information on the right. Available operations are listed on the left and after right clicking. Unavailable operations are hidden automatically to keep interface clean.
Available operations to a partition:
- Resize volume (shrink and extend)
- Move partition location
- Merge two adjacent volumes by 1 step
- Copy volume to unallocated space
- Convert partition between Logical and Primary
- Convert NTFS to FAT32
- Optimize file system to fix error and improve performance
- Change drive letter (such as D:)
- Change label (add or modify name of partition)
- Set as Active
- Check file system integrity
- Defrag to improve performance
- Hide from File Explorer
- Delete (files can be recovered)
- Format volume to use as new
- Wipe (erase data permanently)
- Surface test (scan bad sectors)
- Explore (view files/folders with directory)
- View properties
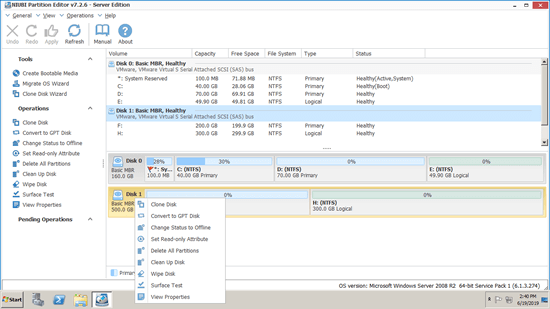
Available operations to whole disk:
- Initialize brand new disk
- Change status to offline or online
- Set read-only attribute
- Wipe disk (cannot be recovered)
- Surface test
- View properties
- Clone disk to migrate data and OS
- Convert MBR disk to GPT
- Delete all partitions
- Cleanup disk
Learn more about this disk partition manager for Windows Server 2008/2012/2016/2019/2022, watch the video guide how to use it.