Because of many advantages of hardware RAID array, many servers are built with RAID. For example, RAID 1 is used for Operating System and programs, so the server could keep online if one of the disk has hardware issue. RAID 5 is another common used type of array, it can be used for both OS and data or only data. This article introduces how to resize/extend RAID partition in Windows Server 2008 R2 without losing data.

Extend RAID partition with diskpart or Disk Management
To Operation System and programs, there is no difference if you use physical hard disk or hardware RAID array. The performance, fault-tolerant and other benefits are realized by RAID controller/card. While extending RAID virtual partition in Windows 2008 server, do not break array or do any operations to controller, no matter you use RAID 0, 1, 5, 10, etc. with any types or brands of RAID controller.
The first thing you should do is backing up, because there is potential data loss risk with both Windows native and third party software. Secondly, check if there is free space in any partition on the same virtual disk, if yes, you can resize and extend RAID partition in Windows Server 2008 easily.
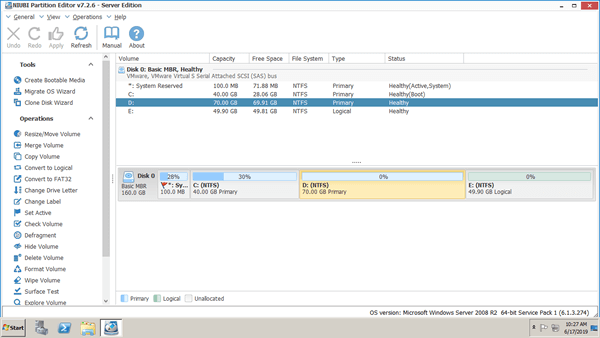
Some people may create several RAID arrays with several hard disks, while resizing RAID partition, the volumes that you want to shrink and extend must be on the same virtual disk. The virtual disk means Disk 0, 1, 2, etc. that are shown by Windows Disk Management or NIUBI Partition Editor.
Windows Server 2008 has two native tools to help extend partition: diskpart command and Disk Management. However, they cannot extend a partition by shrinking any other one. The only way to extend partition is by deleting the right contiguous one, in additional, the partition that you want to extend must be formatted with NTFS. FAT32 and any other types of partitions are not supported.
- How to extend partition with diskpart in Windows Server 2008?
- How to extend volume with Server 2008 Disk Management?
Extend RAID system partition C from D or other volume
In most of servers, the right contiguous partition D (or E) is used for programs or some Windows services, so you cannot delete it. In that case, both native tools are useless. You'd better run third party server partition software.
- Both NTFS and FAT32 partitions can be shrunk and extended without losing data.
- Unallocated space can be made on either left or right when shrinking a partition.
- Unallocated space can be combined to either contiguous partition by 1 step.
- Unallocated space can be moved and combined to any non-adjacent partition on the same disk.
- Many other features such as copy, merge, convert, defrag, hide, wipe, scan partition, etc.
Among these software, NIUBI Partition Editor is much safer and faster because of its unique technologies:
- Virtual Mode - all operations will be listed as pending for preview, real disk partitions won't be modified until click "Apply" to confirm.
- Cancel-at-will - if you applied wrong operations, you can also cancel the ongoing operations without losing data.
- 1 Second Rollback - if any error is detected while resizing partition, it automatically reverts server to original status in a flash.
- Hot Clone - clone disk partition without rebooting to back up or migrate system and data.
- Advanced file-moving algorithm - resize and extend hard drive partition 30% - 300% faster.
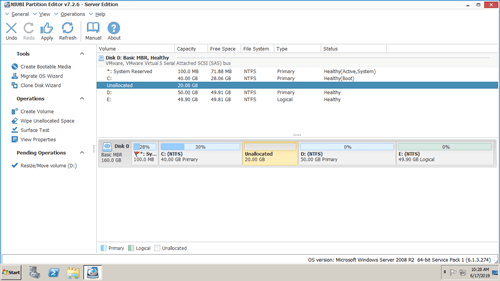
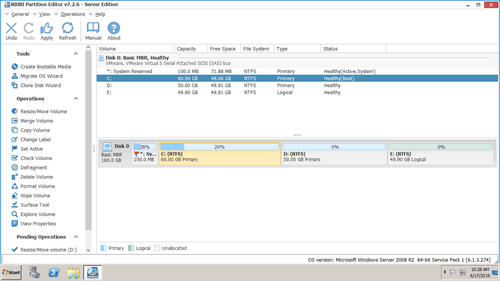
Download NIUBI Partition Editor and you'll see the main window with disk partition structure and other information on the right, available operations to selected disk or partition are listed on the left or by right clicking.
Steps to extend RAID system partition C on Windows Server 2008 R2:
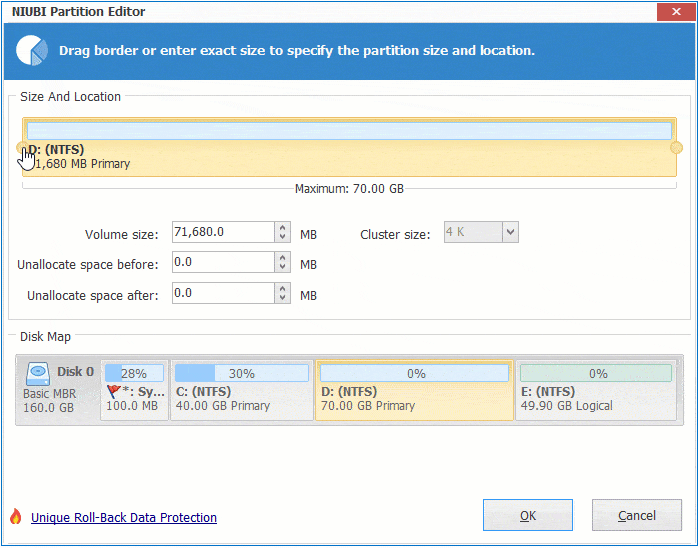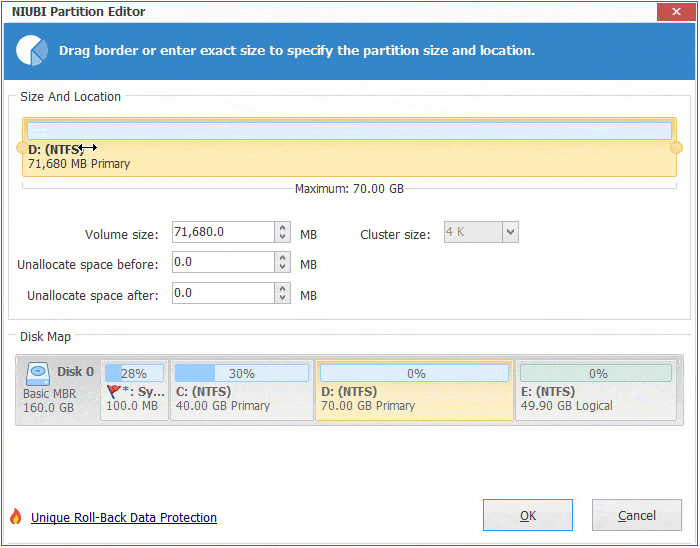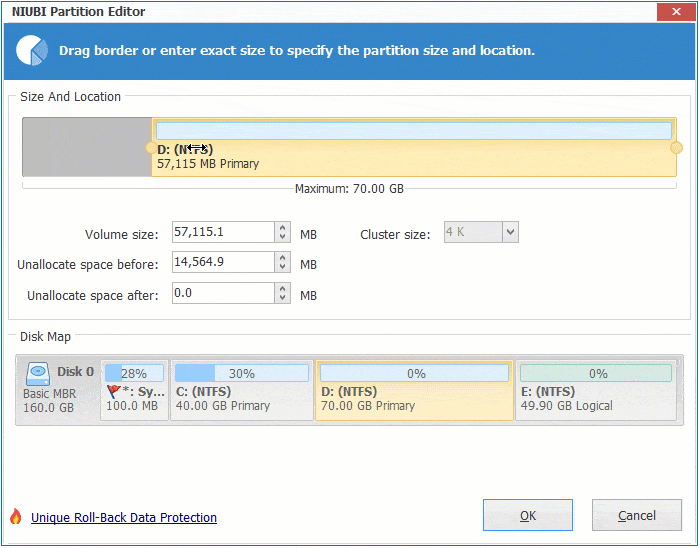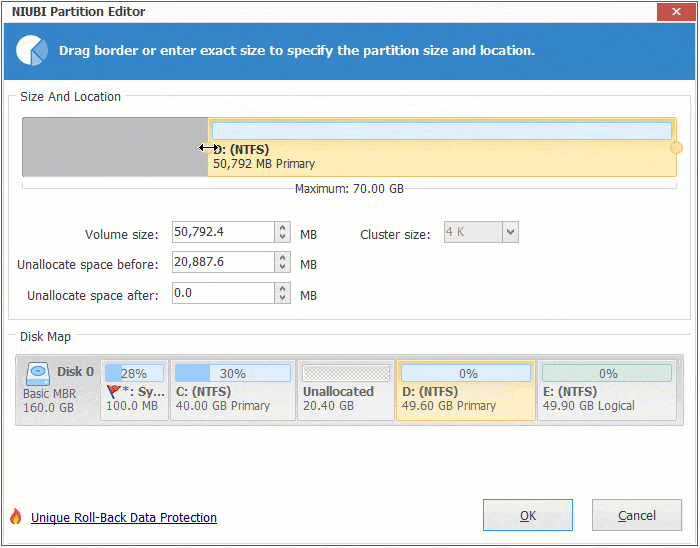
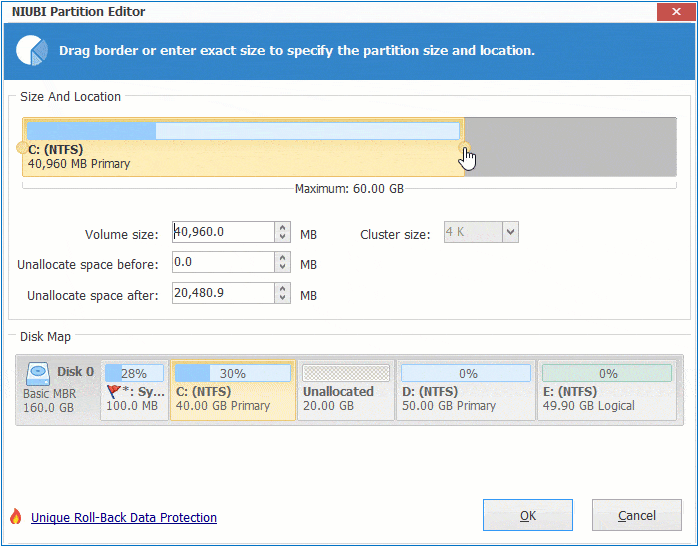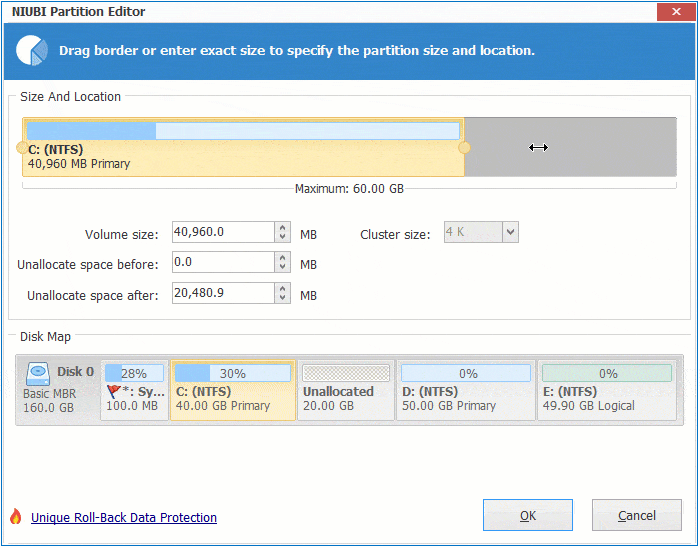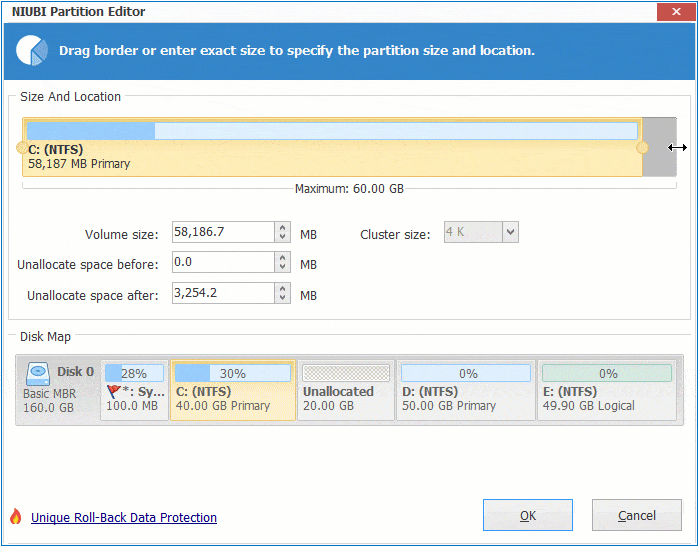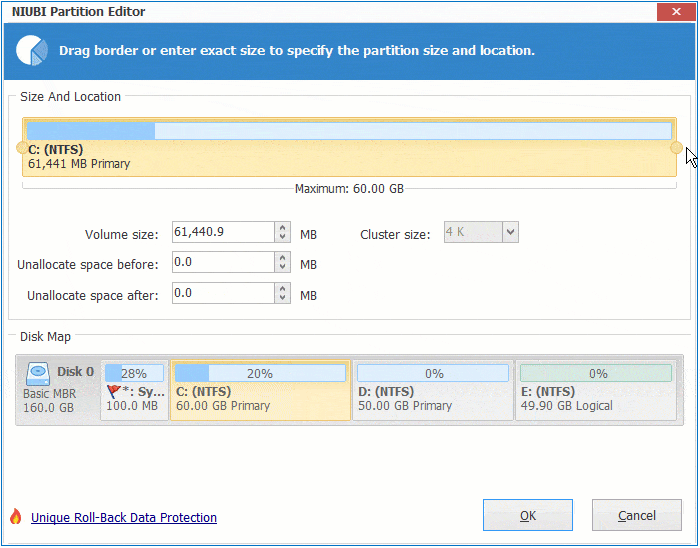
Step 1: Right click the right contiguous partition D: (in some server, it is E:) and select "Resize/Move Volume", drag left border towards right in the pop-up window. You may also enter an amount in the box behind "Unallocated space before".
Step 2: Right click system C: drive and select "Resize/Move Volume", drag right border towards right to combine Unallocated space.
Step 3: Click "Apply" on top left to execute.
Watch the video how to extend physical and RAID partition in Windows Server 2008 R2:
How to increase RAID virtual disk and partition
In some old server, the system disk is small and there may be not enough free unused space on entire RAID virtual disk. In that case, check if your controller support RAID expansion. If yes, additional space will be shown as Unallocated on the end of original virtual disk after rebuilding RAID array with larger disks. Then follow the steps above to combine the Unallocated space to the partitions that you want to extend.
If your RAID controller has no such ability, the size of RAID virtual disk will be the same with before even if you rebuild with larger disks. In that case, follow the steps below:
- Insert a physical hard disk which is larger than the RAID virtual disk.
- Copy from RAID to the physical disk with NIUBI Partition Editor.
- Build another RAID with larger disks.
- From the physical disk to new RAID again.
If you can build a new RAID array and copy from original RAID directly, that will be easier and faster. Remember to change BIOS and boot from the new device after copying.
In most of servers, there is available free space, so you just need to follow the steps in the video to resize and extend RAID partition in Windows Server 2008 with NIUBI Partition Editor.