Disk partitions are allocated while installing Operating System, but sometimes you need to change partition size. For example: shrink a large volume to create more partitions, or extend system C drive when it is getting full. To help resize partition, Microsoft provides "Shrink Volume" and "Extend Volume" functions in Disk Management from Server 2008. However, both functions have many disadvantages. The typical issue is that Disk Management cannot extend a volume by shrinking another one. Windows Server 2012 inherited the same functions without any improvement. Therefore, many people feedback that they cannot extend C drive in Server 2012 R2 with Disk Management, even after shrinking or deleting partition D. This article introduces why Disk Management is unable to extend C drive in Windows Server 2012 R2 and how to solve this problem easily.

Why Disk Management cannot extend C drive in Server 2012 R2
Both Shrink and Extend Volume functions support NTFS partition only. However, it is not an issue to C drive, because system partition is formatted with NTFS by default. The most common reasons why you are unable to extend C: drive in Windows Server 2012 R2 include:
- No contiguous unallocated space on the right
- The adjacent drive (D:) is logical partition.
I'll explain one by one.
Reason 1: No adjacent unallocated space on the right
First of all, you should know that the size of a physical disk is fixed, thus before extending C drive, there must be unallocated space. If you did not delete or shrink another volume to get such space, of course you cannot extend C drive with any tool.
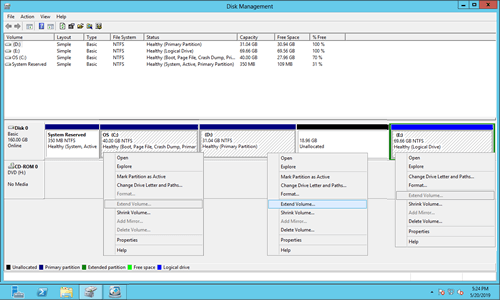
Obviously, it is better to get unallocated space by shrinking a volume, because you won't lose files in it. The problem is that you still cannot expand C drive after shrinking D or other partitions. As you see in my server, Extend Volume is disabled for C drive after shrinking D. This is because:
- "Extend Volume" only works when there's adjacent unallocated space on the right.
- "Shrink Volume" can only make unallocated space on the right while shrinking a partition.
The unallocated space that shrunk from D: drive is nonadjacent to C, so Extend Volume is grayed out. This is the most common reason why you can't extend C drive in Server 2012 (R2) with Disk Management.
Reason 2: The right contiguous partition is logical
This issue only exists on MBR disk, you can ignore this section if you use GPT disk.
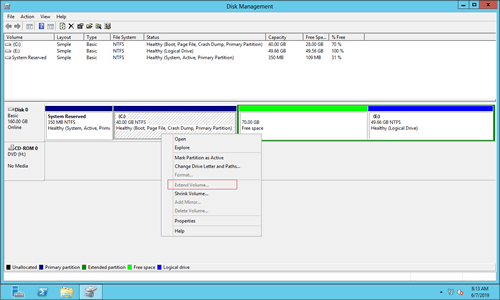
Because Windows Server 2012 cannot extend C drive by shrinking other volume, some people are wondering if it is possible to delete D drive to get contiguous unallocated space. The answer is yes if D is a primary partition. If it is a logical drive, you still cannot extend C drive in Disk Management after deleting.
This is because:
On a MBR style hard disk, you can create maximum 4 primary partitions, or 3 primary partitions plus an extended partition. Extended partition works like a container and all logical partitions should be inside of it. Free space that deleted from logical drive can't be extended to any primary partition. Likewise, unallocated space that deleted from a primary partition can't be extended to any logical partition.
As you see in my test server, disk space of D drive is shown as "Free" instead of "unallocated" after deleting. It is still part of the extended partition, so Extend Volume doesn't work. If you want to convert this free space to unallocated, you must delete all other logical drives and the entire extended partition.
Reason 3: 2TB restriction on MBR disk
Because Windows 2012 server has running for so many years, the system disk is small when building the server. Some people replaced the system disk with a larger one. If this disk is MBR, you cannot extend C drive past 2TB, even if there's adjacent unallocated space on the right.
What to do when unable to extend C drive in Windows Server 2012
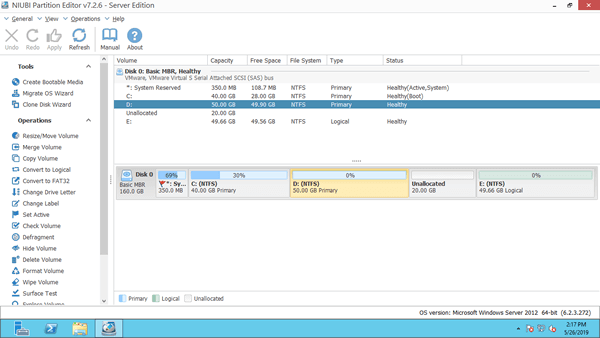
With NIUBI Partition Editor, this problem can be solved easily. It is able to combine unallocated or Free space to either contiguous partition with 1 step. When the unallocated space is nonadjacent, it is able to move it and then combine to other partition on the same disk.
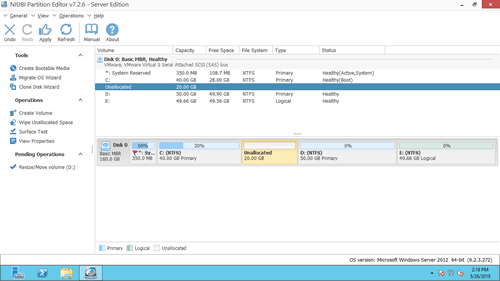
Download it and you'll see the main window with disk partition structure and other information. There is 20GB unallocated space that is shrunk from D drive via Disk Management.
Steps when you are unable to extend C drive in Windows Server 2012 R2 after shrinking D:
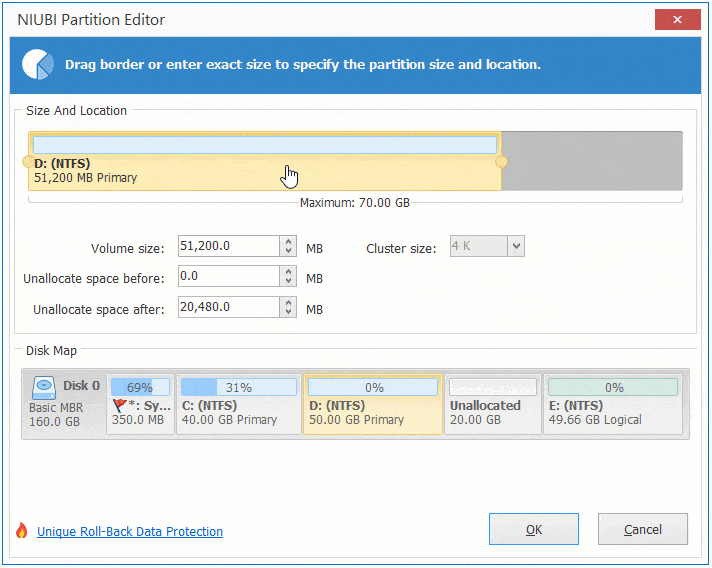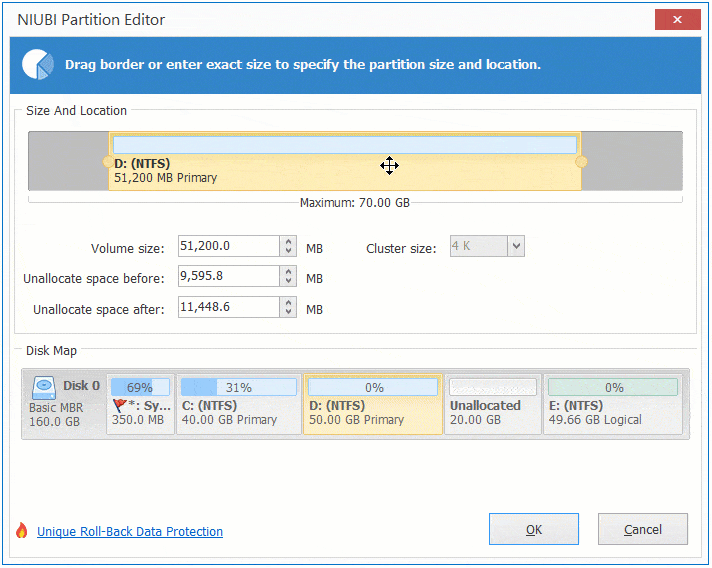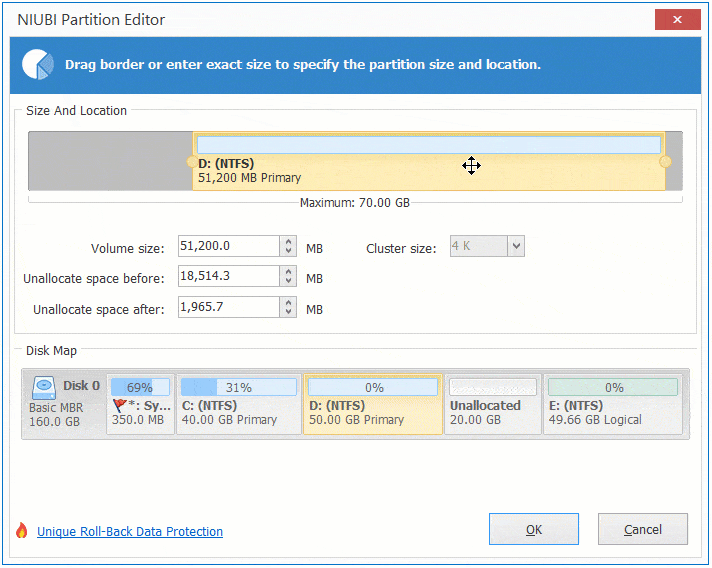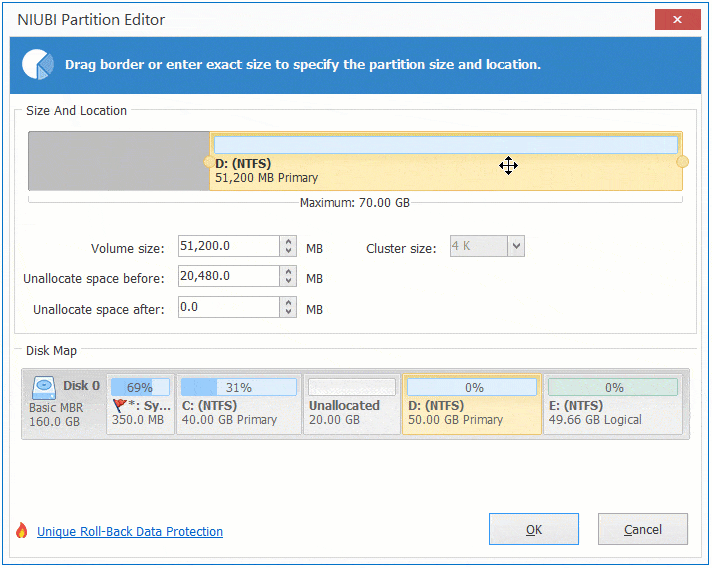
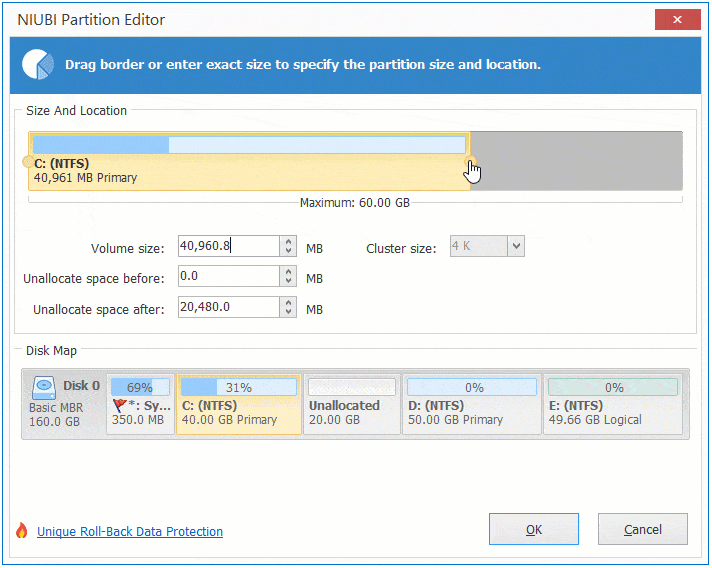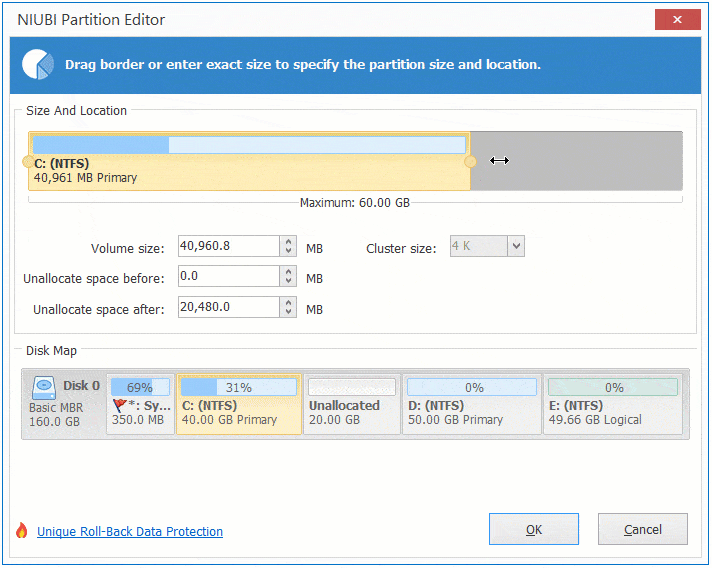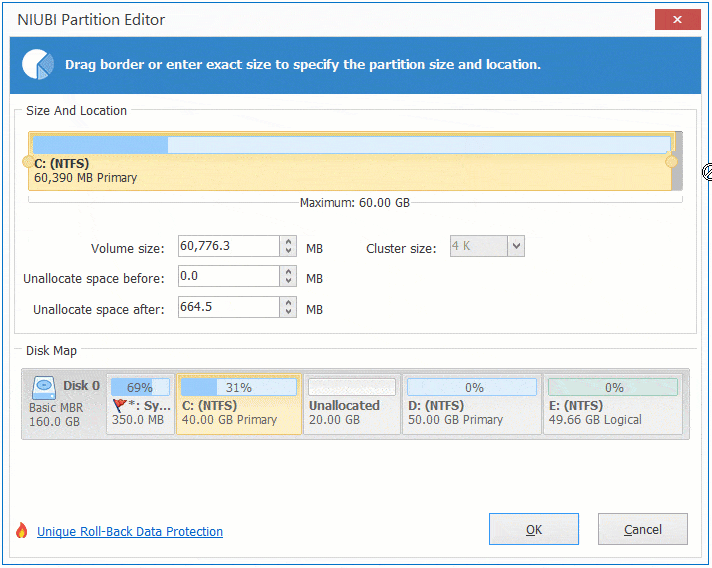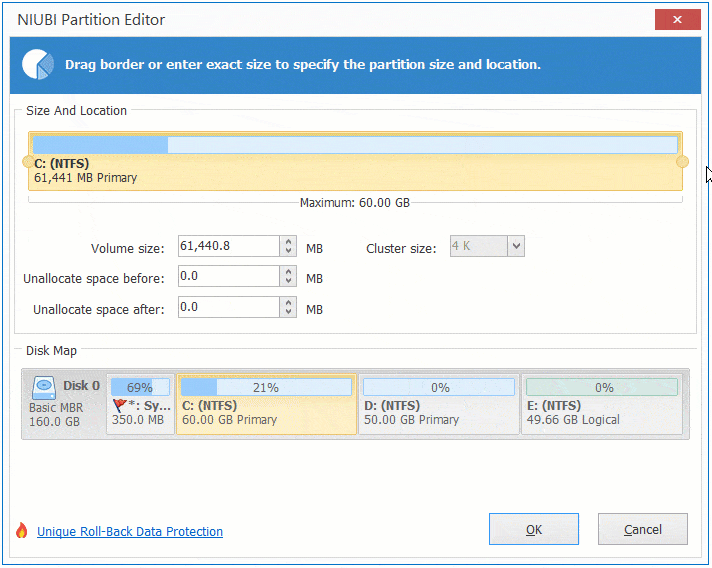
Step 1: Right click D: drive and select "Resize/Move Volume", drag the middle of this partition towards right in the pop-up window:
Step 2: Right click C: drive and select "Resize/Move Volume" again, drag right border towards right in the pop-up window.
Step 3: Click "Apply" on top left to take effect. (All operations before this step only work in virtual mode.)
Watch the video how to move unallocated space and add to C drive:
Steps when you cannot extend C drive in Server 2012 R2 after deleting D:
- Recreate this partition with Windows Disk Management.
- Shrink or delete this partition to get unallocated space with NIUBI Partition Editor. Make unallocated space on the left if you want to shrink this partition.
- Right click C drive and merge unallocated space with "Resize/Move Volume".
Steps when you can't extend C drive in Windows 2012 server past 2TB:
- Follow the steps to convert MBR disk to GPT.
- Run NIUBI Partition Editor to merge or move unallocated space to C drive.
Better than other software, NIUBI Partition Editor has unique 1 Second Rollback, Virtual Mode, Cancel-at-will and Hot Clone technologies to protect your system and data. Besides shrinking, moving and extending partition, it helps you do many other disk partition management operations.